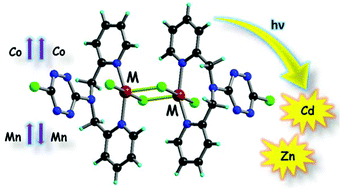
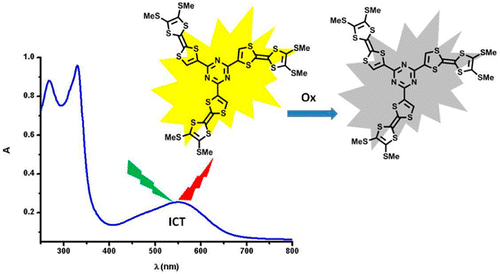
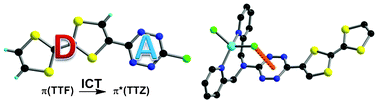
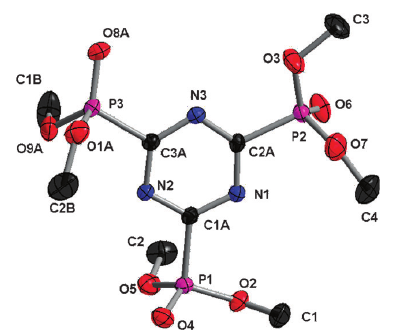
-
Triplet state CPL active helicene-dithiolene platinum bipyridine complexes

T. Biet, T. Cauchy, Q. Sun, J. Ding, A. Hauser, P. Oulevey, T. Bürgi, D. Jacquemin, N. Vanthuyne, J. Crassous and N. Avarvari
Chemical Communications, 53 (66) (2017), p9210-9213


DOI:10.1039/C7CC05198K | unige:96312 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF | Supporting Info
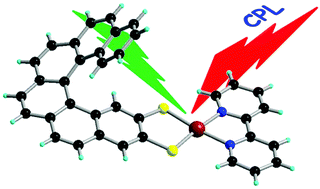
Chiral metal dithiolene complexes represent a family of chiral precursors, which can give rise to molecular materials with properties resulting from the interplay of chirality with conductivity, magnetism, and photophysics. We describe herein the first examples of chiral metal diimine dithiolene complexes, by the use of a platinum(II) centre coordinated by 2,2â-bipyridine and helicene-dithiolene ligands. Straightforward synthesis of racemic and enantiopure complexes allows the preparation of luminescent Pt(bipy) [4] and [6]helicene compounds for which the solid-state structure was determined as well. TD-DFT calculations support the assignment of the low energy bands observed in the UV-vis absorption spectra as mixed metal-ligand-to-ligand charge transfer transitions and confirm that the emission band results from the T1 excited state. Interestingly the enantiopure [6]helicene complexes show CPL activity at room temperature in acetonitrile solutions with anisotropy factors of 3Ã10-4.